Structures in C
Last Updated :
05 Jan, 2023
What is Structure data type?
A structure is a keyword that creates user-defined data types in C/C++. A structure creates a data type that can be used to group items of possibly different types into a single type.
Where to use the Structure data type?
We can use this data type to store dates of different attributes of different data types.
For example, If we want to store data on multiple patients such as patient name, age, and blood group.
How to create a structure?
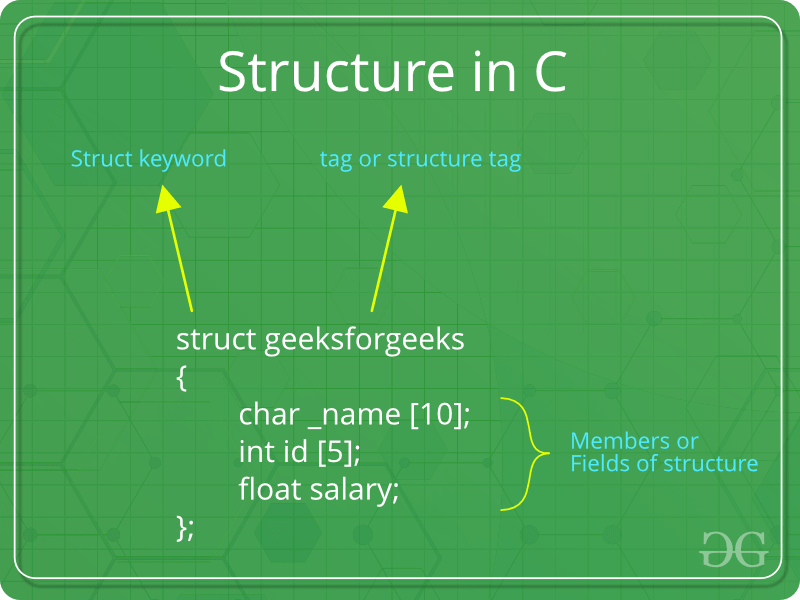
‘struct’ keyword is used to create a structure. Following is an example.
C
struct address
{
char name[50];
char street[100];
char city[50];
char state[20];
int pin;
};
|
How to declare structure variables?
A structure variable can either be declared with structure declaration or as a separate declaration like basic types.
C
struct Point
{
int x, y;
} p1;
struct Point
{
int x, y;
};
int main()
{
struct Point p1;
}
|
Note: In C++, the struct keyword is optional before in declaration of a variable. In C, it is mandatory.
How to initialize structure members?
Structure members cannot be initialized with declaration. For example, the following C program fails in the compilation.
C
struct Point
{
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
};
|
The reason for above error is simple, when a datatype is declared, no memory is allocated for it. Memory is allocated only when variables are created.
Structure members can be initialized using curly braces ‘{}’. For example, the following is a valid initialization.
C
struct Point
{
int x, y;
};
int main()
{
struct Point p1 = {0, 1};
}
|
How to access structure elements?
Structure members are accessed using dot (.) operator.
C
#include <stdio.h>
struct Point {
int x, y;
};
int main()
{
struct Point p1 = { 0, 1 };
p1.x = 20;
printf("x = %d, y = %d", p1.x, p1.y);
return 0;
}
|
What is designated Initialization?
Designated Initialization allows structure members to be initialized in any order. This feature has been added in C99 standard.
C
#include <stdio.h>
struct Point {
int x, y, z;
};
int main()
{
struct Point p1 = { .y = 0, .z = 1, .x = 2 };
struct Point p2 = { .x = 20 };
printf("x = %d, y = %d, z = %d\n", p1.x, p1.y, p1.z);
printf("x = %d", p2.x);
return 0;
}
|
Output
x = 2, y = 0, z = 1
x = 20
This feature is not available in C++ and works only in C.
What is an array of structures?
Like other primitive data types, we can create an array of structures.
C
#include <stdio.h>
struct Point {
int x, y;
};
int main()
{
struct Point arr[10];
arr[0].x = 10;
arr[0].y = 20;
printf("%d %d", arr[0].x, arr[0].y);
return 0;
}
|
What is a structure pointer?
Like primitive types, we can have a pointer to a structure. If we have a pointer to structure, members are accessed using arrow ( -> ) operator.
C
#include <stdio.h>
struct Point {
int x, y;
};
int main()
{
struct Point p1 = { 1, 2 };
struct Point* p2 = &p1;
printf("%d %d", p2->x, p2->y);
return 0;
}
|
What is structure member alignment?
See https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/structure-member-alignment-padding-and-data-packing/
Limitations of C Structures
In C language, Structures provide a method for packing together data of different types. A Structure is a helpful tool to handle a group of logically related data items. However, C structures have some limitations.
- The C structure does not allow the struct data type to be treated like built-in data types:
- We cannot use operators like +,- etc. on Structure variables. For example, consider the following code:
C
struct number {
float x;
};
int main()
{
struct number n1, n2, n3;
n1.x = 4;
n2.x = 3;
n3 = n1 + n2;
return 0;
}
|
But we can use arithmetic operation on structure variables like this.
C
#include <stdio.h>
struct number {
float x;
};
int main()
{
struct number n1, n2, n3;
n1.x = 4;
n2.x = 3;
n3.x = (n1.x) + (n2.x);
printf("\n%f", n3.x);
return 0;
}
|
- No Data Hiding: C Structures do not permit data hiding. Structure members can be accessed by any function, anywhere in the scope of the Structure
- Functions inside Structure: C structures do not permit functions inside Structure
- Static Members: C Structures cannot have static members inside their body
- Access Modifiers: C Programming language does not support access modifiers. So they cannot be used in C Structures.
- Construction creation in Structure: Structures in C cannot have a constructor inside Structures.
Related Article : C Structures vs C++ Structure
We will soon be discussing union and other struct-related topics in C. Please write comments if you find anything incorrect, or you want to share more information about the topic discussed above.
Please Login to comment...